What is SSL?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security technology used for establishing an encrypted link between a browser and the web server. This encrypted link ensures that all the data passed between the browser and web server remain integral and private. SSL now becomes an industry standard and it is used by every website now in the protection of their online transactions.
To create this connection a SSL Certificate is required by the Web Server, when you are going to activate the SSL for your website, while configuration you will be asked to answer a number of questions to verify your website and company etc, so after this simple process the Web Server provides you two cryptographic keys e.g. a public key and a private key.

We don't need to make the public key a secret key, so it will be placed into a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) - a data file also containing the details. Now you have to submit the CSR then. After submission the CA will validate your provided details and on verification will issue an SSL Certificate containing your details that allows you to use SSL. Your web server will be matching your issued SSL Certificate containing your information to your Private Key. It will then be able to establish an encrypted link between your Web Server and your customer's web browser.
The complexities of the SSL protocol will remain hidden for your customers. The browser will be indicating the customers with a key indicator to let them know that they are currently safe and protected by an SSL. And there will be a lock icon in the top left corner of the browser, they can check the SSL Certificate and the details by clicking on the lock icon.
When a user opens the browser and your secure website so then it retrieves the site's SSL Certificate and verify it that it has a valid expiry date and not expired yet, it has been issued by a trusty Certification Authority, and used by the website for which it has been issued from the CA. If any of these check fails the browser displays a warning to the customer/user to let them know that the verification check fails and the site is currently not secured by SSL.
Types of SSL:
Over the last few years a huge number of organizations have increased dramatically using SSL Certificates. As the applicants for SSL are now in a great amount so 3 types of SSL have emerged:
- Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates.
- Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates.
- Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates:
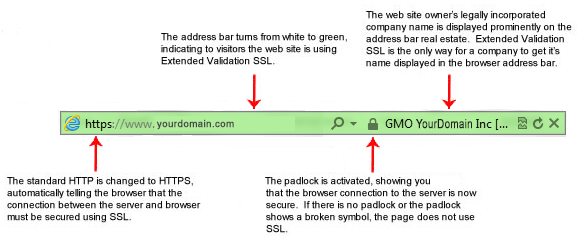
EV is where the Certificate Authority (CA) checks the right of the applicant to use a specific domain name which customer owns PLUS it conducts a THOROUGH vetting of the organization. It is a simple and short process for issuance and clearly defined in the EV Guidelines, as formally ratified by the CA/Browser forum in 2007, the following steps are required by a CA before they issue an SSL Certificate:
- Verification of the physical, legal and operational existence of the entity.
- Verification of entity that all matches official records
- Verification of the rights to use domain specified in the EV SSL Certificate
- Verification of the entity that it has properly authorized the issuance of the EV SSL Certificate
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates are available widely for all types of businesses, e.g. government entities and both unincorporated and incorporated businesses. A second set of guidelines, the EV Audit Guidelines, specify the criteria under which a CA needs to be successfully audited before issuing EV SSL Certificates. These audits are repeated every year to ensure the integrity of the issuance process.
Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates:

OV is where the Certificate Authority (CA) checks the right of the applicant to use a specific domain name which they own PLUS it conducts some vetting of the organization.
Major difference is that the vetted company information could be visible for a customer when clicking on the Secure Site Seal, giving enhanced visibility i.e. who is behind the site and associated enhanced trust etc
Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates:

OV is where the Certificate Authority (CA) checks the right of the applicant to use a specific domain name and in DV no company identity information is vetted, and information is not displayed other than encryption information.
